Table of Contents
Remember those group projects in school where one person did all the work, one never showed up, and everything was finished the night before? That same kind of chaos often happens in real-world teams too. Scrum Methodology helps fix this by giving everyone a clear role, shared goals, and regular check-ins, turning messy teamwork into smooth, steady progress.
Whether you're building software or launching a product, Scrum Methodology keeps teams aligned and organised. This blog explores its basics, key roles, events, artefacts, benefits, and impact on Project Management.
Table of Contents
1) What is Scrum Methodology?
2) How Does Scrum Work?
3) Scrum Methodology and Processes
4) Key Roles Within a Scrum Team
5) Benefits of Scrum Methodology
6) What are Scrum Events?
7) What are Scrum Artefacts?
8) How is Scrum Methodology Helpful in Project Management?
9) Conclusion
What is Scrum Methodology?
Scrum is a way for teams to work together and finish tasks step by step. It helps the team plan the work, do it, check how it went, and make it better next time. Scrum is often used in projects like making software, but it can be used for many types of work.
In Scrum, the team has clear roles and meets often to talk about what they are doing. It also helps the team stay open, solve problems early, and make changes if needed. Scrum helps teams stay on track and finish good work faster.
How Does Scrum Work?
Scrum is easy to understand but takes time to master. Created by Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber, Scrum’s core ideas are explained in The Scrum Guide, which outlines how to apply Scrum effectively.
Key Concepts Include:
1) Self-organising teams that plan and manage their own work
2) Time-boxed Sprints that typically last 1–4 weeks
3) Customer-focused delivery in every Sprint
4) Defined roles with Scrum Master, Product Owner and Developers
5) Regular events such as Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review and Retrospective
6) Core artefacts including Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog and Increment
Scrum Methodology and Processes
The Scrum methodology is built on a simple but powerful process that helps teams stay focused, collaborate effectively, and improve continuously. Here's how it works step by step:
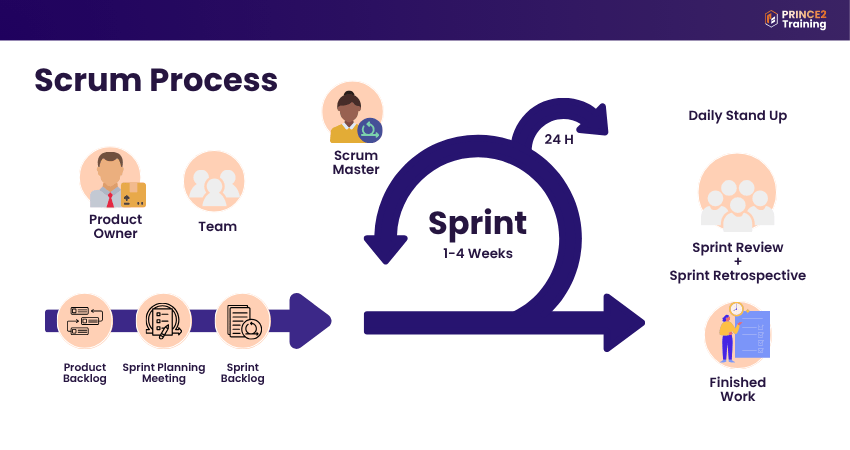
1) Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is a list of everything the product needs. It includes features, fixes, and new ideas. The Product Owner looks after this list. As the team learns more or gets feedback, the list is updated often.
2) Sprint Planning
Before starting a Sprint, the team has a planning meeting. In this meeting, they choose tasks from the Product Backlog to work on in the Sprint. They also set a clear goal and created a smaller list called the Sprint Backlog.
3) Sprint Execution
During the Sprint, the team works on the selected tasks. A Sprint usually lasts between 1 and 4 weeks. The team breaks the work into small, simple parts. Everyone plans and works together to finish the tasks on time.
4) Daily Scrum (Stand-up)
Every day during the Sprint, the team holds a short 15-minute meeting. In this meeting, each person answers three questions: What did I do yesterday? What will I do today? Is anything blocking my work? This helps everyone stay on track.
5) Sprint Review
At the end of the Sprint, the team meets to show the work they finished. They present it to the customer or other stakeholders. The team also gets feedback, which helps plan better for the next Sprint.
6) Sprint Retrospective
After the Sprint Review, the team holds a Retrospective. In this meeting, they talk about what went well and what didn’t. They also discuss how they can do better in the next Sprint. This helps the team improve over time.
7) Increment Delivery
At the end of every Sprint, the team delivers a small part of the product that works. This is called an "increment." It must be fully finished and follow all the agreed rules. The increment can be shown or used right away.
Key Roles Within a Scrum Team
A Scrum team has three roles: Scrum Master, Scrum Product Owner, and Developers. Everyone works together and shares the work. The team is small, about 10 people, to stay clear and productive.
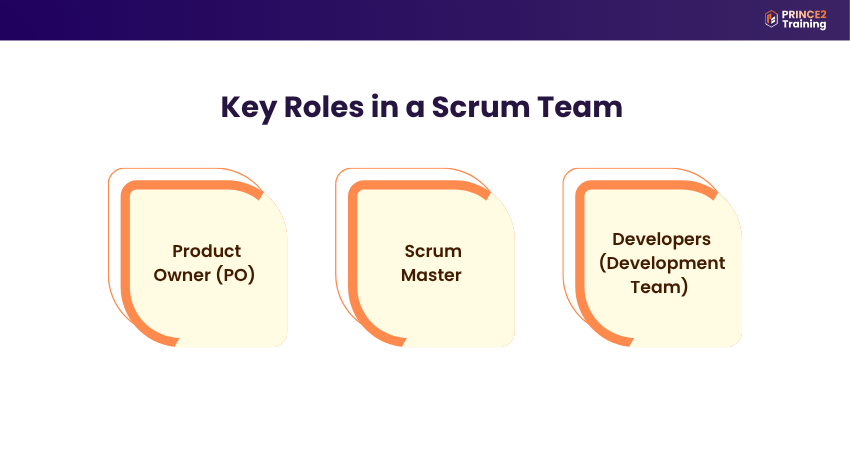
1) Product Owner (PO)
The Product Owner ensures the team is building the right things. They manage the Product Backlog, a list of tasks and ideas for the product. The Product Owner talks to customers and others to understand what is important. They choose what the team should work on next. Only the Product Owner can change the backlog. Everyone must respect their choices.
2) Scrum Master
The Scrum Master helps everyone understand and use Scrum the right way. They guide the team and help them stay on track. The Scrum Master is not the boss; they are more like a coach. They help the team solve problems, work better together, and follow the Scrum process. They also help the Product Owner and even the whole company use Scrum well.
3) Developers (Development Team)
Developers are the people who build the product. They work in the team and do the tasks planned for the Sprint. They help plan the work, build it, and check that it’s done right. Developers follow the rules of quality and help each other every day to reach the goal. The skills they need depend on the work, but their job is to create usable work every Sprint.
Learn essential Scrum Developer skills and build better products faster. Join our Scrum Developer Training now!
Benefits of Scrum Methodology
Scrum helps teams deliver usable work each Sprint, ensuring better quality and efficient use of resources. These are the benefits of Scrum Methodology:
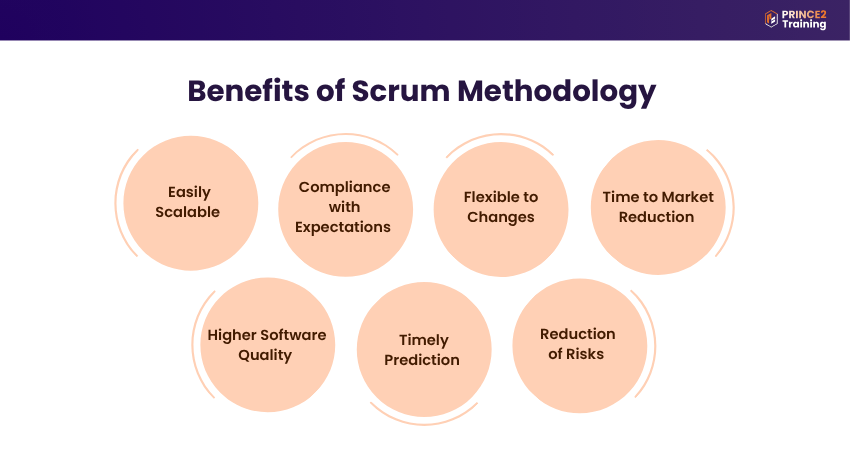
1) Easily Scalable
Scrum uses short work cycles. This helps teams focus on small tasks and do them well together. It also makes it easy to add new ideas, designs, or features in a clear and simple way.
2) Compliance with Expectations
The customer shares what they want and what’s important. The team gives time estimates. The Product Owner sets the task order. At the end of each Sprint, the customer gives feedback.
3) Flexible to Changes
If the customer or market needs change, Scrum can quickly adjust and stay on track. It is made to handle changes during the project without any big trouble.
4) Time to Market Reduction
Because work is done in small, manageable parts, teams can release a working product much faster. Customers can start using it much earlier.
5) Higher Software Quality
Scrum makes teams build a working part of the product in every Sprint with full focus. This helps catch mistakes early and gives much better results.
6) Timely Prediction
Scrum shows how fast the team works in each Sprint with clear tracking and progress updates. This helps the team guess better when future work will be done and delivered.
7) Reduction of Risks
By getting feedback often and making small, smart changes, the chances of failure go down. Problems are seen early and quickly fixed before they become big.
What are Scrum Events?
Scrum Events are regular meetings that the Scrum Team follows in order. These help the team stay on track and work better together. Here are the main Scrum Events:
1) Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is the first meeting before a Sprint starts. In this meeting, the team decides what tasks they will work on during the Sprint. They also set simple and clear goals. By the end of the meeting, everyone understands what needs to be done and how they will do it.
2) Sprint
A Sprint is the time when the team works to finish their tasks. It usually lasts about 2 weeks, but can be smaller or longer depending on the project. If the work is more difficult or unclear, a shorter Sprint is better so the team can check progress often.
3) Daily Scrum or Stand-up
The Daily Scrum is a short meeting held every day, usually for 15 minutes. In this meeting, each team members say what they finished, what they are going to do next, and if they have any problems. It is called a "stand-up" because it’s quick, and people usually stand during it.
4) Sprint Review
At the end of the Sprint, the team have a Sprint Review. In this meeting, they show the work they completed to the customer or stakeholders. The team gets feedback, and the Product Owner may update the task list for the next Sprint.
5) Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective happens after the Sprint Review. The team talks about what went well and what didn’t. They share ideas to make the next Sprint better. This meeting helps the team improve their work every time.
Learn Scrum roles, tools, and processes from certified industry professionals. Join our Scrum Master Certification now!
What are Scrum Artefacts?
Scrum Teams use special tools called artefacts to help plan, manage, and finish their work. These tools give clear information to the team and to others about what is being done. There are three main Scrum Artefacts:
1) Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is a list of everything that needs to be done for the project. It includes features, ideas, fixes, and changes. It's the team’s big to-do list. The list keeps changing as new things are added or old ones removed. The Product Owner updates this list often.
2) Sprint Backlog
The Sprint Backlog is a smaller list taken from the Product Backlog. It shows the tasks the team plans to do during the current Sprint. Before each Sprint, the team picks the tasks they will work on. This list can change a little during the Sprint if needed.
3) Product Increment
An Increment is the finished work at the end of a Sprint. It is a working part of the product that can be used or shown. Each Sprint should give a useful result. The team may work in different ways, but they always aim to meet their Sprint Goal.
How is Scrum Methodology Helpful in Project Management?
Scrum is not just for software. It can help in many types of projects. Here’s how it helps in Project Management:
1) Increased Customer Satisfaction
1) Customers give feedback after each Sprint
2) Their ideas help shape the product from the start
3) This leads to a better product, happier customers and value from their investment
4) Customers feel more involved and valued throughout the project
2) High-quality Products
1) Teams meet customers every 2 weeks in Sprint Reviews
2) Feedback is used to make quick updates
3) This helps create a product that meets real needs
4) Regular updates improve the product step by step
3) Lowers Risk and Focus on Greater Control
1) Everyone knows their roles and timeline
2) Regular team talks help find problems early
3) Fewer surprises mean smoother project flow
4) Risks are managed better because progress is tracked often
4. Organisational Collaboration Through Innovation and Creativity
1) People from different roles work as one team
2) They share skills, ideas, and solutions
3) This leads to smart ideas and a better final product
4) Working together builds trust and a stronger team spirit
Conclusion
Scrum Methodology helps teams stay organised, deliver work faster, and respond easily to changes. It brings clear roles, regular check-ins, and better teamwork. Whether in software or other industries, Scrum supports smooth Project Management. Also, ensure your investment of time and resources leads to high-quality results. If you're looking for a simple, effective way to manage projects, the Scrum framework is a great place to start.
Become a skilled Product Owner and maximise product value today. Join our Scrum Product Owner Certification now!




 Back
Back


 Back to
topics
Back to
topics









