Table of Contents

Starting a project feels exciting until confusion and delays start appearing. It often happens when there is no clear system to guide the work. That is why Project Management Methodologies are important. They help teams stay organised, reduce stress, and keep progress smooth from beginning to end.
In this blog, you will learn what Project Management Methodologies are, discover the top ones used by successful teams, and understand how to choose the right fit for your project. Get ready to explore practical approaches that make project delivery simpler, faster, and more successful.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Project Management Methodology?
2) Most Popular Project Management Methodologies
a) Agile Methodology
b) Scrum Methodology
c) Waterfall Methodology
d) Six Sigma Methodology
e) PRINCE2 Methodology
f) Kanban Methodology
g) Scrumban Methodology
h) Lean Project Management Methodology
i) Extreme Programming (XP)
j) Outcome Mapping
3) Choosing the Right Project Management Methodology
4) Conclusion
What is a Project Management Methodology?
Project Management Methodology is a structured framework that guides how projects are planned, executed, monitored, and completed. It outlines the processes, tools, roles, and best practices that teams should follow to deliver successful outcomes, making Project Management Methodologies essential for organised and effective delivery.
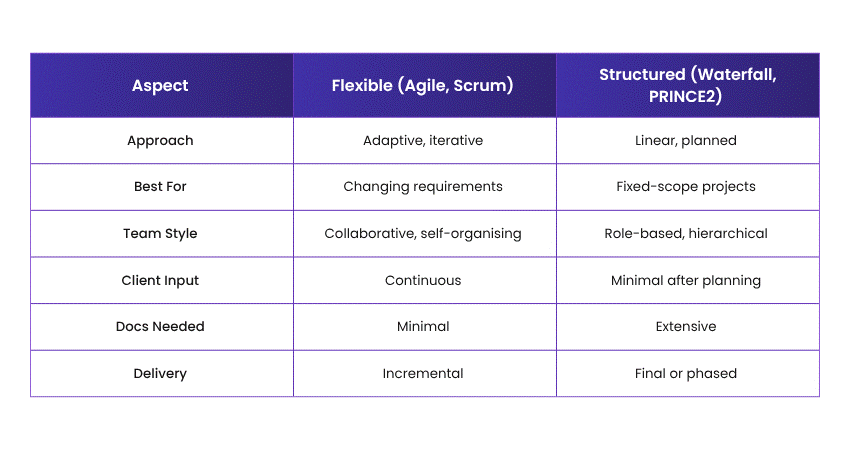
Different Project Management Methodologies offer different strengths. Some are highly structured, such as Waterfall or PRINCE2, while others are more flexible and adaptive, like Agile or Scrum. This allows organisations to choose an approach that aligns with team capabilities, stakeholder expectations, and overall project complexity.
Key Features are:
1) Brings consistency, clarity, and control to project work
2) Ensures everyone knows their roles, timelines, and goals
3) Improves communication and reduces errors
4) Boosts project success rates
Methodology Choice Depends on:
1) Project size and complexity
2) Industry standards
3) Level of collaboration and change expected
Most Popular Project Management Methodologies
Here are some of the popular Project Management Methodologies that offer a positive impact on your project.
1) Agile Methodology
Agile is a flexible, iterative approach to Project Management that focuses on collaboration, customer feedback, and rapid delivery. Work is divided into small, manageable cycles known as sprints, allowing for regular evaluation and adjustment.
Agile encourages close teamwork, active stakeholder involvement, and the frequent delivery of usable outcomes. This makes it particularly well-suited to fast-paced environments such as Software Development and creative industries.
1) Best For: Software development, startups, changing environments
2) Benefits: Faster delivery, continuous improvement, high team involvement
2) Scrum Methodology
Scrum is an Agile framework that operates in short, time-boxed iterations called sprints. It involves clearly defined roles such as the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and team members. Key events include daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives.
It is highly effective for projects that benefit from rapid iterations and continuous feedback, particularly in Software Development and tech-driven teams.
1) Best For: Software products, iterative development, digital solutions
2) Benefits: Stage boundaries, business justification, clearly defined roles
3) Waterfall Methodology
A traditional, linear approach where each phase like, requirements, design, implementation, testing, and deployment, must be completed before the next begins. It works best for projects with a well-defined scope and minimal changes.
However, its rigidity makes it less suited for projects requiring frequent changes. This Project Methodology is common in construction, engineering, and regulated industries.
1) Best For: Construction, manufacturing, fixed-scope IT projects
2) Downside: Difficult to adapt to change once started
4) Six Sigma Methodology
A quality-focused approach that uses Statistical Analysis to reduce defects and improve process consistency. It follows DMAIC and is heavily used in manufacturing and production to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma improves process reliability and cycle time, which leads to higher customer satisfaction.

1) Core Process: DMAIC for Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control
2) Used in: Manufacturing, healthcare, operations
5) PRINCE2 Methodology
A structured, process-driven methodology is used widely in the UK and Europe. PRINCE2 divides projects into manageable stages with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
PRINCE2 focuses on documentation, risk management, and governance, making it ideal for projects requiring control, predictability, and formal reporting.
1) Best For: Government, public sector, large enterprises
2) Key Features: Stage boundaries, business justification, and clearly defined roles
Achieve project Agility and structure by joining PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation and Practitioner Training now!
6) Kanban Methodology
Kanban uses a visual board (physical or digital) to manage tasks and workflow. It limits work-in-progress (WIP) to avoid bottlenecks and focuses on continuous delivery.
It’s often used in software maintenance, support teams, and lean environments. Kanban promotes flexibility, quick turnaround, and real-time tracking.
1) Tools: Kanban boards, cards, swimlanes
2) Best For: Maintenance, support, service delivery teams
7) Scrumban Methodology
A hybrid of Scrum and Kanban, Scrumban combines the structured roles and sprints of Scrum with Kanban’s visual flow and flexibility.
It suits teams transitioning from Scrum or those needing iterative planning with continuous delivery. It’s ideal for evolving, service-oriented teams.
1) Best For: Teams transitioning from Scrum to continuous flow
2) Features: No fixed sprints, pull-based task selection
8) Lean Project Management Methodology
Lean Project Management focuses on maximising value while minimising waste. Originally developed for manufacturing, Lean has been widely adopted in Software Development, healthcare, and service industries.
The methodology emphasises continuous improvement, customer value, and the elimination of non-essential activities
1) Used in: Manufacturing, product design, services
2) Tools: Value stream mapping, continuous improvement (Kaizen)
9) Extreme Programming (XP)
XP (Extreme Programming) is an Agile Software Development framework focused on enhancing software quality and responsiveness to changing requirements. Core practices include pair programming, Test-driven Development (TDD), small and frequent releases, and continuous integration.XP promotes strong development practices like TDD, refactoring, and CI. It is particularly well-suited to software teams that require rapid changes and high code reliability.
1) Best For: High-risk software projects
2) Benefits: High code quality, rapid changes, close customer involvement
10) Outcome Mapping
Common in international development and nonprofit sectors, Outcome Mapping focuses on the behavioural changes of stakeholders rather than tangible deliverables. It tracks progress through indicators of influence and changes rather than outputs or timelines.
It involves setting long-term visions, identifying boundary partners, and tracking outcomes related to behaviour, actions, and relationships. It’s a flexible, people-centred planning approach.
1) Used in: Social impact and development projects
2) Key Tools: Intentional design, outcome journals, performance tracking
Start your Project Management journey with PRINCE2® Foundation Training and build strong foundational skills.
11) PMI's PMBOK
PMBOK is a set of standards and best practices developed by the Project Management Institute. It outlines process groups like Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring, and Closing. PMBOK 6 outlines 10 knowledge areas, while PMBOK 7 focuses on performance domains.
It is a global benchmark and forms the basis for PMP certification. PMBOK is a guide for structured project execution and is the foundation for the globally respected PMP certification.
1) Used For: PMP certification, global projects
2) Key Concepts: Scope, time, cost, quality, risk, stakeholder management
12) Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM is a scheduling technique used to identify the longest chain of dependent tasks, like the critical path. It is to determine the shortest project duration.
It helps Project Managers allocate resources effectively and avoid delays. It’s commonly used in construction, engineering, and large-scale scheduling projects.

1) Best for: Projects with fixed deadlines
2) Use: Schedule optimisation, resource prioritisation
13) Crystal Methodology
Crystal is a family of Agile methodologies that adapts based on team size and project criticality. It values people, interaction, and frequent delivery over tools and rigid processes.
It encourages minimal documentation and emphasises communication. Crystal promotes simplicity, close collaboration, and flexible workflows, making it ideal for small to mid-sized teams.
1) Best For: Small teams, creative projects
2) Types: Crystal Clear, Crystal Orange, Crystal Red (based on team size)
14) Adaptive Project Framework (APF) Methodology
APF is suited for evolving projects where stakeholder feedback after each cycle is used to refine priorities and project direction.. It embraces flexibility by allowing scope to evolve based on stakeholder feedback and project performance.
APF is iterative, meaning the project is completed in cycles, and each cycle ends with a review to assess progress and redefine priorities.
1) Best For: Unpredictable, evolving projects
2) Process: Cycle-based reviews, evolving project scope
15) Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
CCPM is a time-based Project Management method that focuses on resource availability rather than task order. It was developed from the Theory of Constraints (TOC) and aims to address common scheduling issues such as multitasking and inefficient resource allocation.
CCPM uses buffers at the project, feeding, and resource levels to protect critical tasks and prevent delays.
1) Best For: Projects with limited resources and tight timelines
2) Key Concepts: Resource leveling, project buffer, feeding buffer
Become a confident Project Manager by earning PRINCE2® Foundation & Practitioner Training today.
Choosing the Right Project Management Methodology
Selecting the right Project Management Methodology depends on your project goals, size, team structure, and industry needs. The factors below will help you pick the most suitable Project Management Methodologies for successful results.
1) Project Size and Complexity:
Small and simple projects usually work well with lightweight approaches such as Crystal Clear, Kanban, or Lean. For large or difficult projects that require detailed planning and documentation, methods like PRINCE2, PMBOK, or Waterfall are more suitable.
2) Nature of the Work:
If the work changes often or involves creative development, such as in software or startup environments, Agile, Scrum, or XP provide flexibility. Predictable and repeatable work in construction or manufacturing is better matched with Waterfall, CPM, or Six Sigma.
3) Stakeholder Involvement:
Projects needing regular client feedback work well with methods like Scrum, DSDM, or APF. When involvement is low, structured options such as Waterfall or PRINCE2 are better. Choosing the right Project Management Methodologies ensures the project runs smoothly.
4) Flexibility vs Structure:
Agile-based methods support ongoing changes and adaptability, making them ideal for evolving requirements. More structured frameworks like PMBOK or PRINCE2 offer stronger governance and control in regulated environments.
5) Resource Availability:
Teams with limited resources or heavy multitasking may choose CCPM for effective constraint management. Lean is one of the Project Management Methodologies that works best when the focus is on optimising value and reducing waste.
6) Industry Standards:
Some industries prefer specific methodologies: Waterfall and CPM in construction and engineering, PRINCE2 for government projects, Agile and Scrum in IT/software, and Six Sigma or Lean in manufacturing and quality management.
7) Team Experience and Culture:
Experienced teams may succeed with flexible approaches such as Scrumban or XP. Teams needing clarity in roles and processes benefit from Scrum, PRINCE2, or structured PMBOK-based practices.
8) Time and Budget Constraints:
For fixed deadlines or strict budgets, DSDM or Lean and Critical Path Method (CPM) help prioritise essential features. Fully planned approaches like Waterfall and PRINCE2 are suitable when project constraints must be clear upfront.
9) Risk and Compliance:
High-risk or regulated environments benefit from detailed documentation and strong controls using PMBOK PRINCE2. Low-risk or experimental work can use lighter methods like Crystal, Kanban, or Agile.
10) Hybrid Approaches:
No single methodology works for every situation. Many organisations choose hybrid approaches such as Scrumban (Scrum + Kanban), Water-Scrum-Fall (Waterfall planning + Agile delivery), or Agile combined with PMBOK to balance flexibility and structure.
Conclusion
Finding the right Project Management Methodologies is like picking the perfect pair of shoes; it needs to fit your style, support your goals, and help you move forward with ease. Don’t stress about getting it perfect, just start with what feels right and adjust as you go. The real win? A happier team, smoother projects, and results you’re proud of. You've got this, now go lead your project like a pro!
Boost your project skills with trusted PRINCE2® Certification and become a confident professional everyone relies on.




 Back
Back


 Back to
topics
Back to
topics









