Table of Contents

The more massive and complex a project, the steeper the uphill battle to finish it without missing a beat. The secret often lies in embracing the Critical Path Method (CPM). Like a GPS for your project timeline, it maps out the longest route of tasks that must be completed on time to avoid delays.
By pinpointing which activities matter most, CPM helps prevent delays, manage costs and bring clarity to even the busiest schedules. So whether you are building skyscrapers or launching software, the Critical Path Method is the key to successful Project Management. This blog shows precisely why it works. So read on and master this game-changer for efficient project execution!
Table of Contents
1) What is Critical Path Method in Project Management?
2) Why is the Critical Path Method Important?
3) How to Find the Critical Path of Project?
4) How to Use the Critical Path Method?
5) When to Use the Critical Path Analysis?
6) Critical Path Method and PERT
7) Critical Path Method and Gantt Chart
8) Advantages of Critical Path Method (CPM)
9) Disadvantages of Critical Path Method (CPM)
10) Conclusion
What is Critical Path Method in Project Management?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a Project Management technique that Project Managers use to create an accurate project schedule. The CPM method, also known as Critical Path Analysis (CPA) or Critical Path Scheduling, consists of using the critical path diagram to represent the task sequences of a project visually. Once these task sequences or paths are defined, their duration is calculated using the critical path algorithm to identify the critical path.
Why is the Critical Path Method Important?
Projects involve tasks of varying complexity and effort. This is where CPM comes in. It helps you identify priority activities, compare planned versus actual timelines and allocate resources. It supports efficient Resource Management and smoother workflows by highlighting delays, progress and tasks on track.
Bottlenecks can stall dependent activities and slow overall progress. CPM maps task sequences and parallel activities, ensuring accurate time estimates and preventing delays. This structured approach improves scheduling, minimises risks and keeps projects on track with deadlines.
How to Find the Critical Path of Project?
Here are the proven steps through which you can determine a project’s critical path:

1) List Project Activities
Create a work breakdown structure to gather all project activities leading to the final deliverable, then compile a task list with their estimated durations, measured in days. For realistic estimates, draw on past project data, team input, and expert insights.
2) Identify Task Dependencies
Identify tasks that cannot start until others are completed and include a “preceding tasks” column in the task list. Rely on your judgement and team input, since correctly defining dependencies is essential for an accurate critical path diagram.
3) Create a Network Diagram
The next step is to transform the work breakdown structure into a network diagram, a flowchart that shows the sequence of critical path activities. Represent each task with a box and use arrows to illustrate dependencies. Continue adding time-specific components until the overall project schedule is clear.
4) Estimate Task Duration
To calculate the critical path, which represents the longest sequence of dependent tasks, the first step is to estimate the duration of each activity. These estimates can be made using previous project data or established industry standards. Another reliable method is applying the forward pass and backward pass technique.
The forward pass calculates the Earliest Start (ES) and Earliest Finish (EF) times. The backward pass, on the other hand, determines the Latest Start (LS) and Latest Finish (LF) times by working backwards from the final scheduled activity. This ensures deadlines are met and resources are used effectively.
5) Calculate Float (Total vs Free)
Float refers to the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting the early start of its successor or breaking a schedule constraint. It depends on how long the task takes and the time available before the next activity begins.
For example, if a task requires four days and only four days are available before the following activity, it has zero float and becomes critical. Conversely, if a task takes one day but has five days before the next activity starts, it holds float. That makes it non-critical and allows for some flexibility in scheduling.
Turn every project into impactful success stories with our PRINCE2® Certification – Register now!
How to Use the Critical Path Method?
These are the key steps to follow when using the Critical Path Method in Project Management:
1) Compress Schedules
1) Schedule compression is used to evaluate if the project duration can be reduced by adjusting time and cost trade-offs.
2) CPM helps identify interdependent activities and assess whether reducing time is financially viable.
3) It enables Project Managers to minimise project duration by allocating additional resources at an optimal cost.
4) Activities with negative floats may require extra resources to reduce delays.
5) The process of reducing activity time by increasing costs is called crashing.
6) Only critical activities are targeted for crashing, starting with the least expensive option.
2) Resource Levelling and Allocation
1) CPM can be applied for resource levelling, a technique that adjusts schedules to optimise resource allocation.
2) Resource levelling balances resource demand and supply by adjusting deadlines within given constraints.
3) It is mainly used when workforce availability is limited.
4) Levelling utilises available float to adjust resource allocation effectively.
5) It reduces pressure on limited resources while balancing project duration and cost.
6) Critical Path Analysis is widely used in industries where activity durations can be predicted.
Common applications include Construction, Defence, equipment installation, Engineering, Aerospace, plant maintenance or relocation, space launches, Traffic Management, and other large-scale projects.
3) Compile Data for Future Projects
1) The CPM schedule is flexible since it relies on estimated activity durations.
2) The original critical path can be compared with the actual critical path during project execution.
3) Insights from this comparison help refine and improve task duration estimates for future projects.
4) Regular monitoring of the critical path helps identify delays early and take corrective actions.
5) Tracking variances between planned and actual timelines improves overall project control.
6) Lessons learned from schedule adjustments can improve the forecasting accuracy and resource planning in upcoming projects.

When to Use the Critical Path Analysis?
Critical Path Analysis is widely applied in industries with complex projects, such as Aerospace, Defence, Construction, and Product Development. So, it’s best used in Project Management when you need to do the following:
1) Plan complex projects with multiple interdependent tasks. CPA helps identify the longest sequence of tasks that must be completed on time for the entire project to finish as scheduled.
2) Optimise scheduling and resource allocation, especially when deadlines are tight or resources are limited.
3) Identify task priorities and focus on activities that directly impact the project timeline.
4) Assess delays and risks which allows you to adjust plans proactively.
Elevate your Project Management approach by blending traditional control with agile speed. Learn how in our PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation Training - Sign up now!
Critical Path Method and PERT
CPM and Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are powerful Project Management techniques. Here are their key differences:
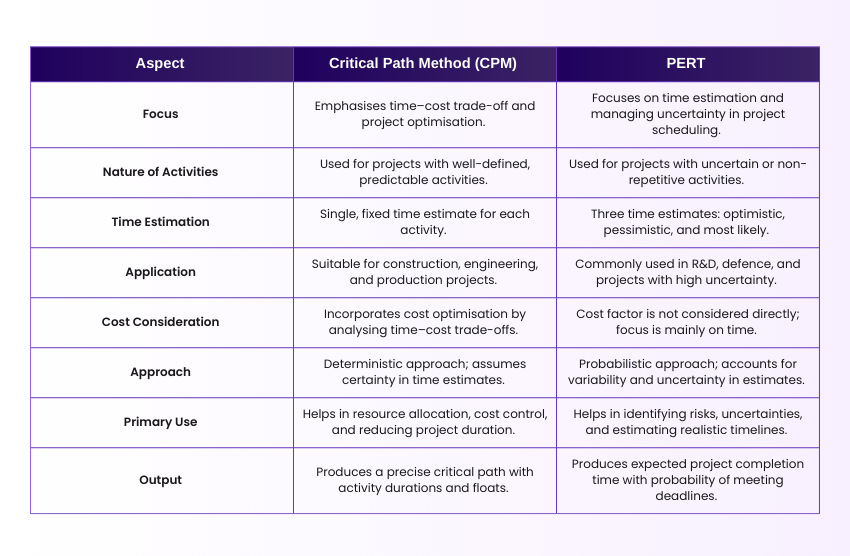
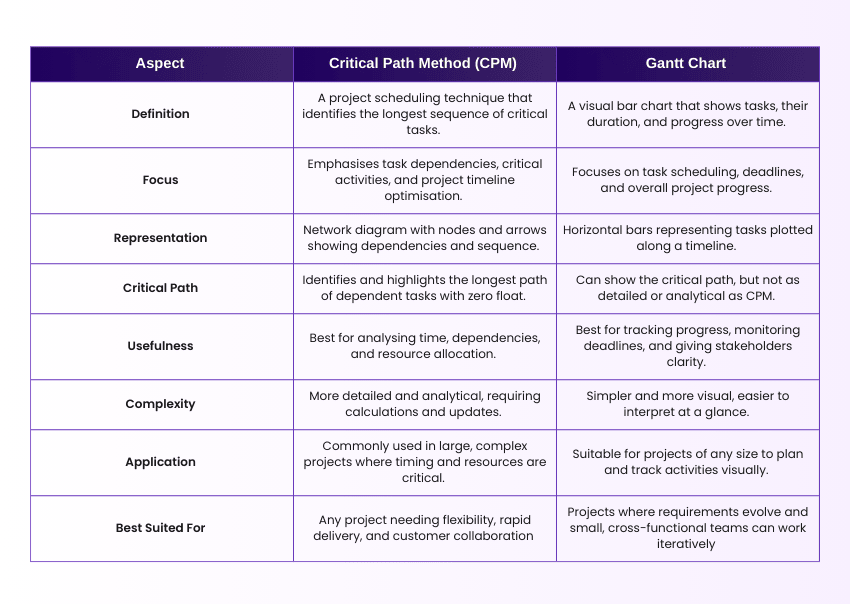
Critical Path Method and Gantt Chart
Gantt charts are visual timelines in the form of horizontal bars that outline project activities and track their progress over time. Like CPM, they also display the dependencies between different tasks within a project. Here are their key differences:
Advantages of Critical Path Method (CPM)
Here are the key benefits of Critical path Method in Project Management:
1) Parallel Task Identification: CPM shows which tasks can be done at the same time.
2) Highlighting Critical Activities: It helps Project Managers spot the most important parts of a project.
3) Improved Communication: CPM makes it easier to explain project plans, timelines, and costs.
4) Proactive Requirement Planning: It looks at requirements in advance to ensure efficient project completion.
5) Accurate Time and Cost Estimation: CPM helps estimate the time and budget needed to finish a project.
Disadvantages of Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method is not without some disadvantages. Here are the main ones to consider:
1) Time-consuming for Complex Projects: CPM can be time-consuming and hard to use for complex projects.
2) Complicated Networks in Large Projects: The networks become complicated in very large projects.
3) Limited Flexibility for Plan Changes: It struggles to handle sudden plan changes, as redrawing the chart is difficult.
4) Ineffective for Individual Scheduling: CPM cannot manage individual team members’ schedules effectively.
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method gives Project Managers the power to see what truly drives success. By spotlighting the tasks that matter most, it turns deadlines into achievable milestones. With CPM, even the most complex projects find rhythm, balance and flow, thus leading teams confidently toward timely, successful completion.
Take your first step toward mastering the art of lasting project success. Sign up for our Introduction to Project Management Course now!




 Back
Back


 Back to
topics
Back to
topics









